System Certification
No.1 of certification consulting performance in Korea, the consulting institution registered at the MSS
No.1 of certification consulting performance in Korea, the consulting institution registered at the MSS

1. Problems with the existing food safety system
2. Need for international standards
As trade between countries increases, the need for food safety standards integration is growing.
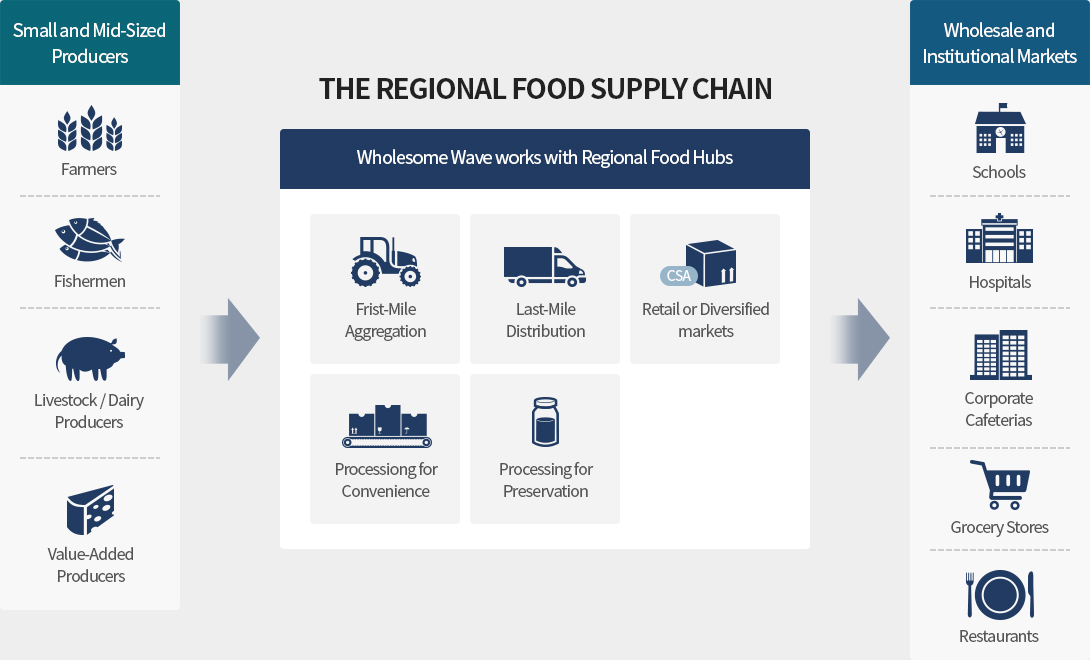
3. Growing need for and scope of food supply chain management
Management of the entire supply chain is required to ensure food safety and prevent food hazards (e.g. raw materials, packaging, equipment, distribution, sanitation services, drugs, etc.).
4. Increasing consumer awareness
More emphasis on safety, consistency of quality, and value for money.
1. Need for certification
2. Utilizing the certification
3. Eligible for certification
1. Increased utility as a food supplier management tool
2. Increased awareness regarding the importance of overall food chain management in the center of individual business site management
3. Expected to become a universal certification standard in the food sector
4. Food Safe System → Total Food Safe Management System
Food Safe System → Total Food Safe Management System
5. In the future, the government is expected to lead the way in converging the HACCP system, and food industry certification by the existing ISO certification body will converge to FSSC 22000
1. Objectives
2. ISO 22000 vs FSSC 22000
| Sort | ISO 22000 | FSSC 22000 |
|---|---|---|
| Applicable standard | KS Q ISO 22000 : 2009 / ISO 22000 : 2005 | FSSC 22000 : Food-Ver3 : 2013 |
| Basic requirements |
|
ISO 22000 Requirements + Industry-specific PRPs (ISO 22002-1: 2011, ISO 22002-4, etc.) + FSSC additional requirements
|
| Certification | Any certification body registered under the national accreditation body in any country can be certified. | The Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is a non-profit organization that governs accreditation organizations. As such, certification organizations cannot easily participate. |
2. FSSC 22000 certification procedure